Triple Rule Used to Describe Codon
Explanation of the Codons Animation. The anti-codon matches complementary bases in the mRNA sequenceTo determine the overall anti-codon sequence that will match a strand of mRNA simply retranscribe the RNA sequence.

The Genetic Code Codon Table Article Khan Academy
Our data suggest that efficient mRNA translation is determined by a triplet-of-triplet genetic code.

. The coding strand turns gray and then disappears leaving the template strand see strands above. If it is a match the amino acid on this new tRNA will be bound to the existing amino acid and the ribosome will shift to the next. Most codons specify an amino acid.
Since there are 64 combinations of 4 nucleotides taken three at a time and only 20 amino acids the code is degenerate more than one codon per amino acid in most cases. When one or two nucleotides were inserted protein synthesis was completely abolished. These nucleotide triplets are called codons.
Up to 24 cash back Step 1. UAU - Tyr UAC - Tyr UAA - UAG - UGU - Cys. Learn how groups of three nucleotides called codons specify amino.
The cell reads the sequence of the gene in groups of three bases. It describes the relationship between DNA s sequence bases A C G and T in a gene and the corresponding protein sequence that it encodes. Codons must always be read from 5 to 3.
One start codon AUG marks the beginning of a protein and also encodes the amino acid methionine. The nucleotide triplet that encodes an amino acid is called a codon. In particular find the smallest power of 4 21 which turns out to be 3.
Codons are made up of any triplet combination of the four nitrogenous bases adenine A guanine G cytosine C or uracil U. That would give you one different amino acid and one extra amino acid in the chain. After DNA is transcribed into RNA the RNA is translated into a polypeptide sequence.
The term used to describe the twisted ladder shape of DNA is. The adaptor molecule for translation is tRNA. For the Codons animation the left-most two base pairs are hidden leaving exactly five 3-base codons 15 base pairs.
Each tRNA has a set of three bases on it known as an anti-codon. Some amino acids are encoded by more than one codon which acts as a. Therefore the first approach was made.
A triplet code could make a genetic code for 64 different combinations 4 X 4 X 4 genetic code and provide plenty of information in the DNA molecule to specify the placement of all 20 amino acids. In other words write out the complementary bases. Supporting all amino acids plus a stop codon requires at least 21 distinct codon values.
A three-nucleotide unit on a strand of mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid is called a _____ codon. A codon is a triple sequence of DNA and RNA that corresponds to a specific Amino acid. Three stop codons mark the end of a protein.
Every three nucleotides in the RNA sequence is read as a separate codon which encodes a specific amino acid. Each group of three nucleotides encodes one amino acid. When experiments were performed to crack the genetic code it was found to be a code that was triplet.
But it was not known which codon synthesizes which amino acid. Codon A codon is a trinucleotide sequence of DNA or RNA that corresponds to a specific amino acid. In this article we will discuss about the approaches made for codon assignments.
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material DNA or mRNA sequences of nucleotide triplets or codons into proteinsTranslation is accomplished by the ribosome which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger RNA mRNA using transfer RNA tRNA molecules to carry. NOTE - starting VarNomen version 3 the is used to indicate a translation stop codon replacing the X used previously see Background. This is why codons are known as the triplet code.
Codons in an mRNA are read during translation. For protein synthesis to work the codon on the mRNA must match the anticodon on the tRNA. Codon Assignment with Unknown Sequences.
Of the 64 possible codon sequences 61 specify the 20 amino acids that make up proteins and three are stop signals. How is the information in an mRNA sequence decoded to make a polypeptide. Decode the DNA sequence.
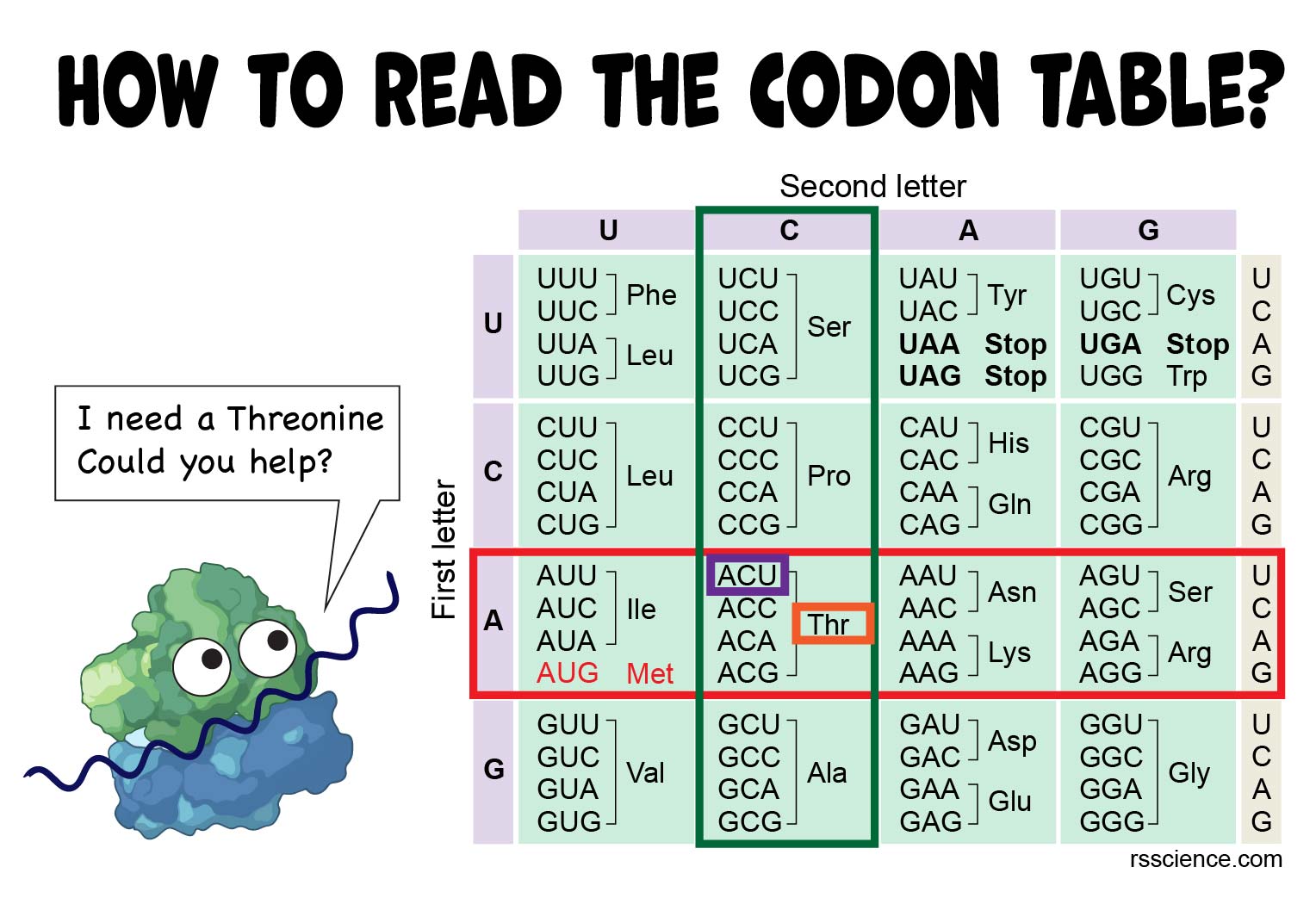
Cells decode mRNAs by reading their nucleotides in groups of three called codons. Use your new code in this case it is AUG to read the chart. The first rule is somewhat basic.
Here are some features of codons. The number of codon values is roughly triple the number or amino acids plus a stop codon allowing for redundancy. It will change one codon completely and introduce an extra codon.
How do you find the codon anticodon. It says that since mRNA is translated in the 5 to 3 direction the codon sequences must occur in a similar orientation so that they will be properly translated. The genetic code describes the relationship between the sequence of DNA bases A C G and T in a gene and the corresponding protein sequence that it encodes.
The genetic code is described as triple code and degenerate. Most images show 17 base pairs. These three letter codes of nucleotides AUG.
When three nucleotides were inserted the protein was synthesized and functional. Triple code coz 3 bases specify each amino acid. This simply means that the first base of a codon must be located at the 5-most end of the codon.
Which amino acid is synonymous with the start codon for translation. Theoretically it was considered that genetic code should be triplet so that codons must be assigned for 20 amino acids. CAA GGG AGU UAU.
It is degenrate coz most of the 20 possible amino acids are determined by more than one codon differentiate between the differences of transcription and. An example of a codon is the sequence AUG which specifies the amino acid methionine. First second third U C A G.
An anticodonThe anticodon is the group of three adjacent bases in a strand of transfer RNA tRNA that will be opposite anti- a codon of. Again how much that would affect the final protein depends on where it happens in the chain. UCU - Ser UCC - Ser UCA - Ser UCG - Ser.
That is the efficiency of translating a particular codon is influenced by the nature of the immediately adjacent flanking codons. Nucleotide position in codon. Each three nucleotides triplet in the genetic code known as a codon encodes a specific amino acid or stop signal.
How you begin to read the chart is you look at the left hand column in the row of A since that is your first letter in the code. Deleting a whole codon again leaves most of the protein chain unchanged. Anti-codons in the template strand are identified as groups of three bases.
UUU - Phe UUC - Phe UUA - Leu UUG - Leu. This demonstrated that three nucleotides specify each amino acid. The various codon arrangements had no apparent effects on flgM mRNA stability or predicted mRNA secondary structures.
Once matched the ribosome will bring in the next tRNA since it can hold two at a time and match it with the next codon. If your DNA sequence is TAC then when you decode it it will translate into the RNA AUG.
How To Read The Amino Acids Codon Chart Genetic Code And Mrna Translation Rs Science
Why A Triplet Code Gene Expression Part 1 Reading Genes To Make Proteins Passel

No comments for "Triple Rule Used to Describe Codon"
Post a Comment